Purchasing a home can be an overwhelming process. One crucial aspect of the home buying journey is finding the right mortgage loan with a suitable interest rate. Understanding mortgage rates and their influencing factors is vital to ensuring that you get the best deal for your situation. In this blog post, we’ll explore the key factors that influence mortgage rates, such as economic and market factors, borrower-specific factors, property-specific factors, and government policies.
Recommended: Get Ready to Move: The Top Houston Houses for Sale in 2023 Expert Realtor Advice: How to Choose the Best Real Estate Professional for Your Needs
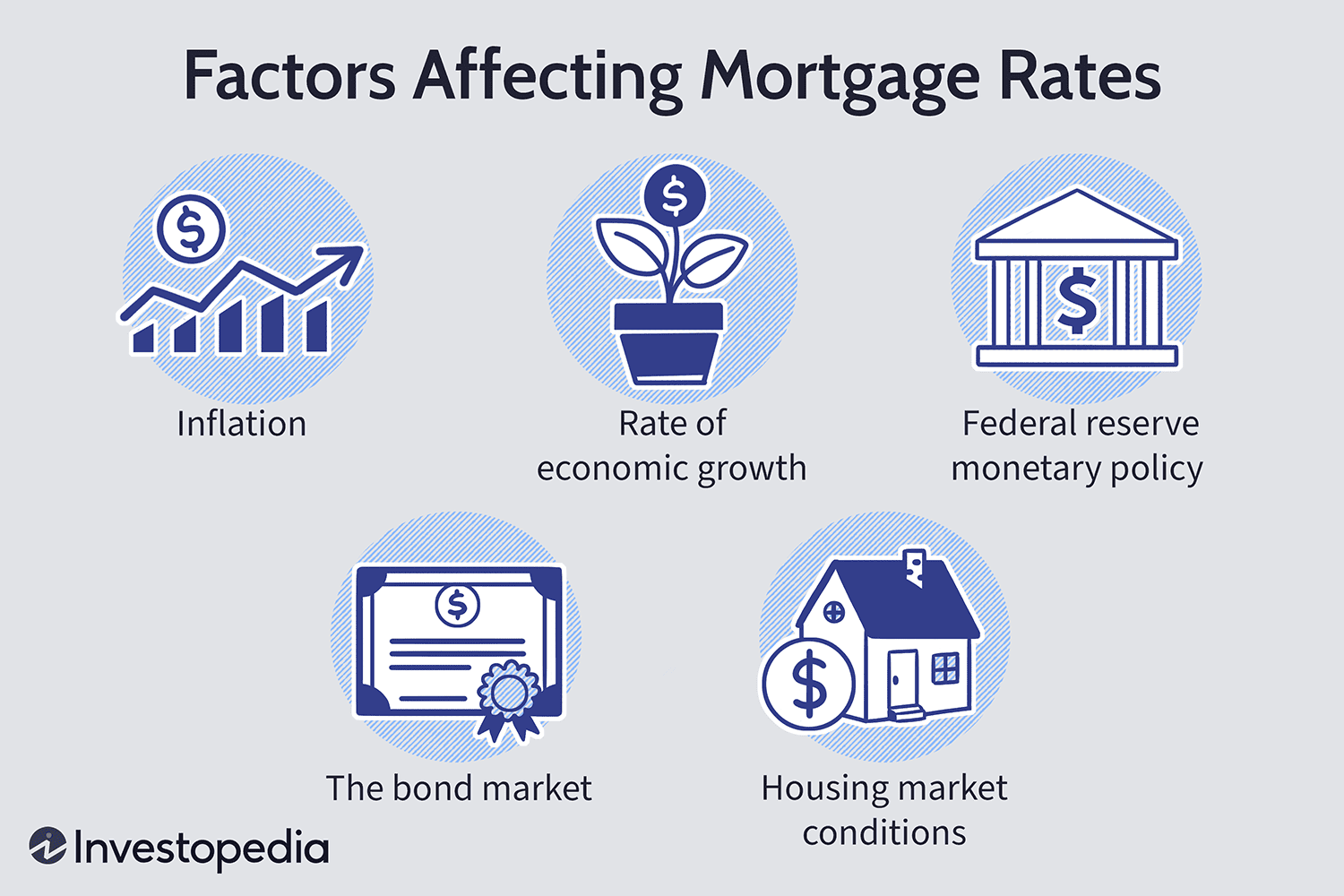
Economic Factors:
Economic factors such as inflation, interest rates, unemployment rate, and GDP play a significant role in mortgage rates. When the economy is booming, inflation is high, and the GDP is growing, mortgage rates tend to rise. The opposite happens when the economy is slowing down. The Federal Reserve Bank’s monetary policy affects interest rates, which impact mortgage rates. When the Federal Reserve increases interest rates, mortgage rates tend to increase, and vice versa. Unemployment rates also impact mortgage rates. A low unemployment rate indicates a strong economy, which means higher mortgage rates.
Market Factors:
Market factors such as supply and demand, competition among lenders, and mortgage-backed securities also influence mortgage rates. When there is high demand for mortgages, the rates tend to rise, and when there is low demand, the rates tend to fall. The competition among lenders also affects mortgage rates, as lenders may offer lower rates to attract borrowers. Mortgage-backed securities are bonds that are secured by mortgages, and they can also affect mortgage rates.
Borrower-Specific Factors:
Borrower-specific factors such as credit score, loan-to-value ratio, debt-to-income ratio, and employment history also influence mortgage rates. Borrowers with higher credit scores tend to receive lower mortgage rates. A lower loan-to-value ratio and debt-to-income ratio may also result in lower rates. Employment history also plays a role in determining mortgage rates.
Property-Specific Factors:
Property-specific factors such as property location, type, and condition also impact mortgage rates. The location of the property can affect rates, with higher rates in areas with higher housing demand. The type of property, such as a single-family home or a condominium, may also affect the rates. The condition of the property may also be considered when determining rates.
Government Policies:
Government policies, such as Federal Reserve policies, housing market regulations, and tax laws, also influence mortgage rates. As mentioned earlier, the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy affects interest rates and, in turn, mortgage rates. Housing market regulations, such as the Dodd-Frank Act, may also impact mortgage rates. Tax laws, such as mortgage interest deductions, may also play a role in determining mortgage rates.
Conclusion:
Understanding the factors that influence mortgage rates can help you make informed decisions when purchasing a home. Keep in mind that mortgage rates can vary depending on your situation, such as first-time homebuyers, investment properties, or self-employed individuals. Utilizing a mortgage rate comparison tool can help you find the best rates for your unique situation. Whether you’re looking for the lowest mortgage rates for refinancing, VA mortgage rates for veterans, or FHA mortgage rates for low down payments, understanding the influencing factors can help you secure the best deal.



Leave a Reply